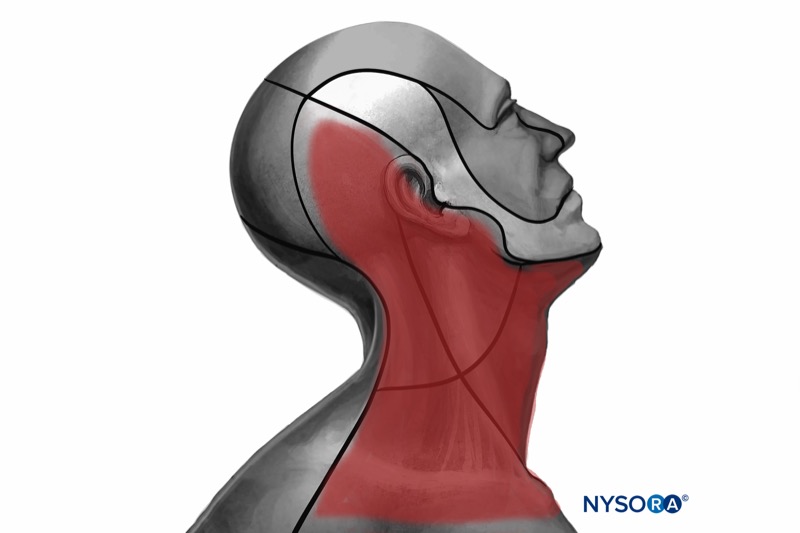
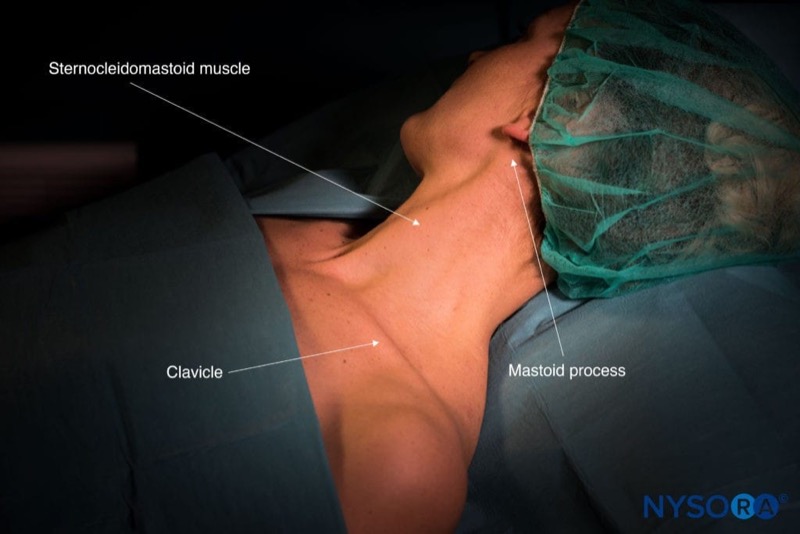
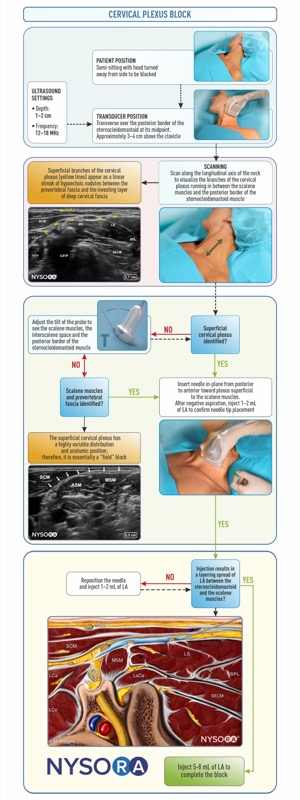
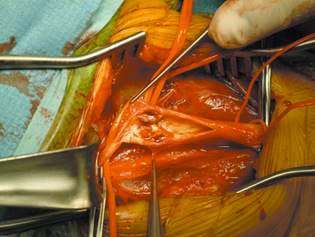
General considerations:
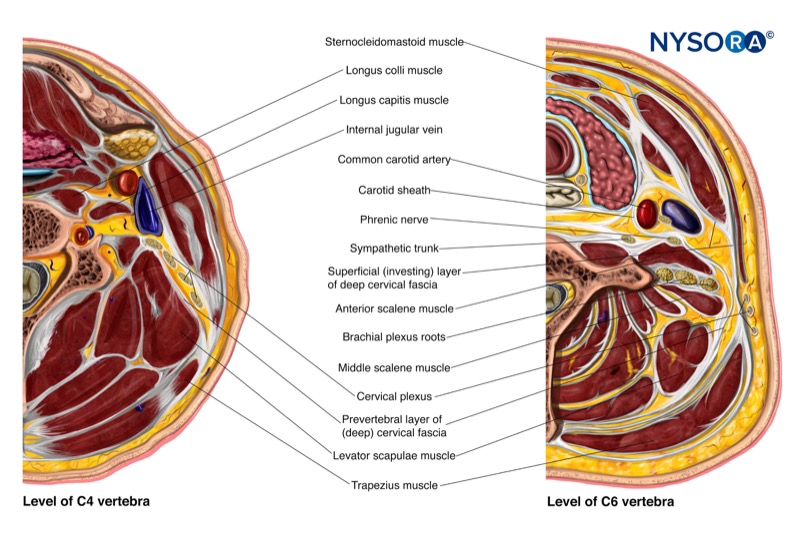
- For a deep injection: Local anesthetic is injected at the C2-C4 level. This technique blocks the entire plexus and is generally not recommended due to the high risk of complications.
- For an intermediate injection: Local anesthetic is injected at the C4-C5 level, between the prevertebral fascia and the investing layer of the deep cervical fascia, under the sternocleidomastoid muscle (SCM). This is the most common technique used in clinical practice.
- For a superficial injection: Local anesthetic is injected at the level of C6, subcutaneously, superficial to the investing layer of the deep cervical fascia.
INTERMEDIATE CERVICAL PLEXUS BLOCK
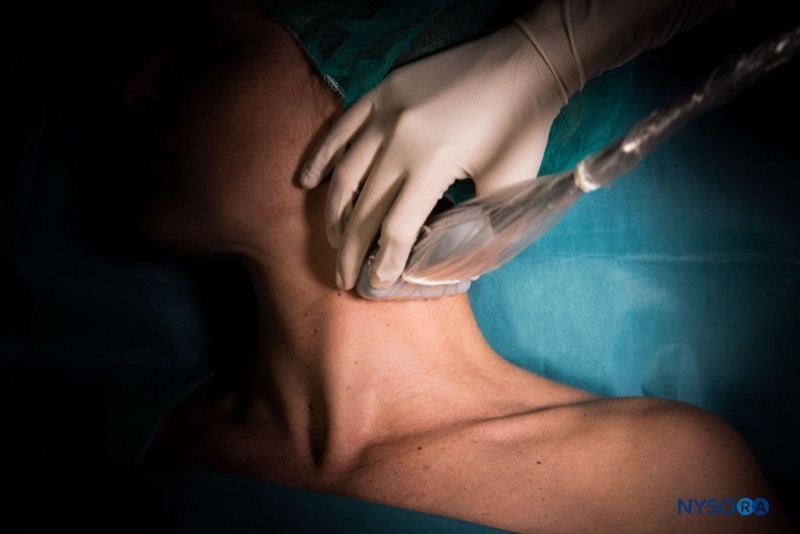
Transducer position
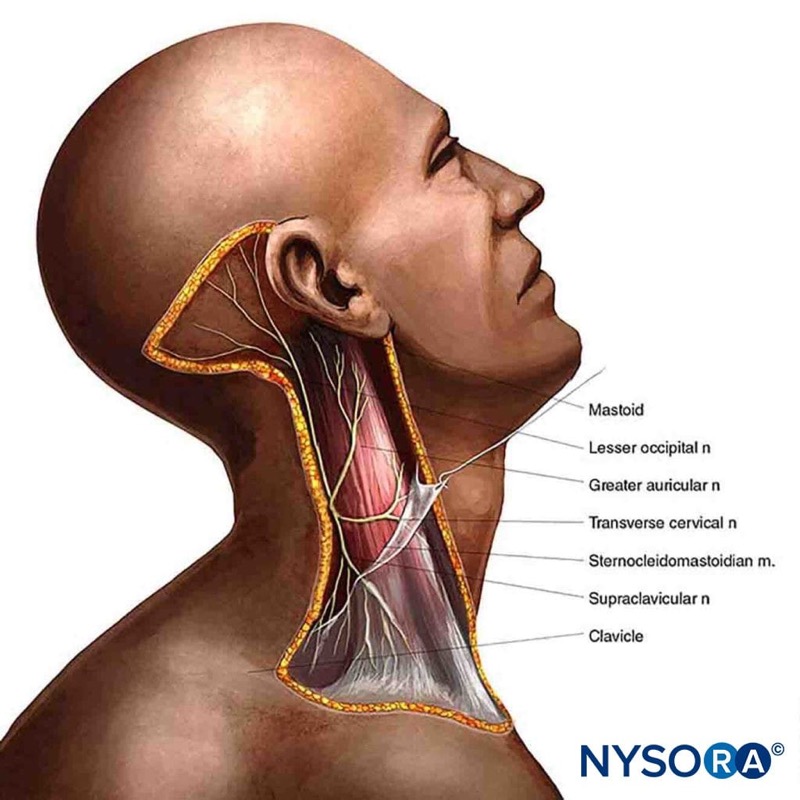
Transverse over the lateral aspect of the neck, overlying the SCM at the midpoint between the mastoid process and clavicle.
Scanning
- Identify the SCM and place the posterior edge in the middle of the screen.
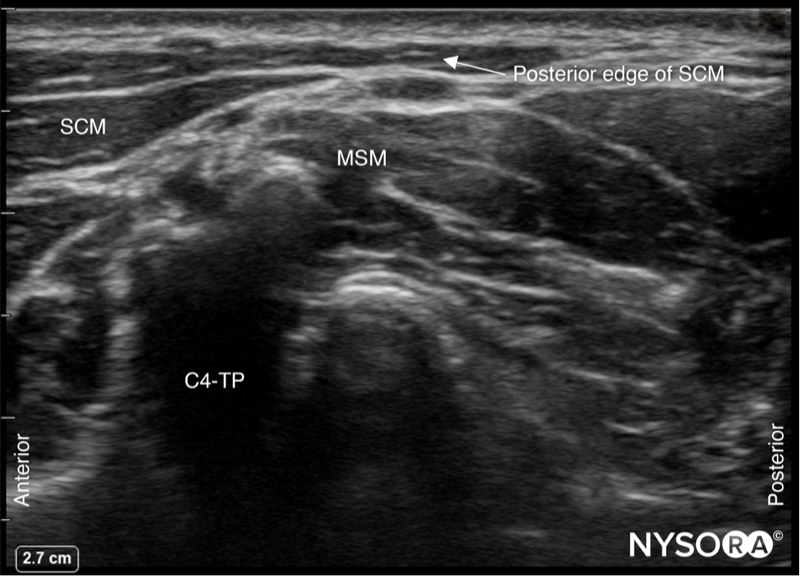
SCM, sternocleidomastoid muscle; MSM, middle scalene muscle; C4-TP, transverse process of C4.
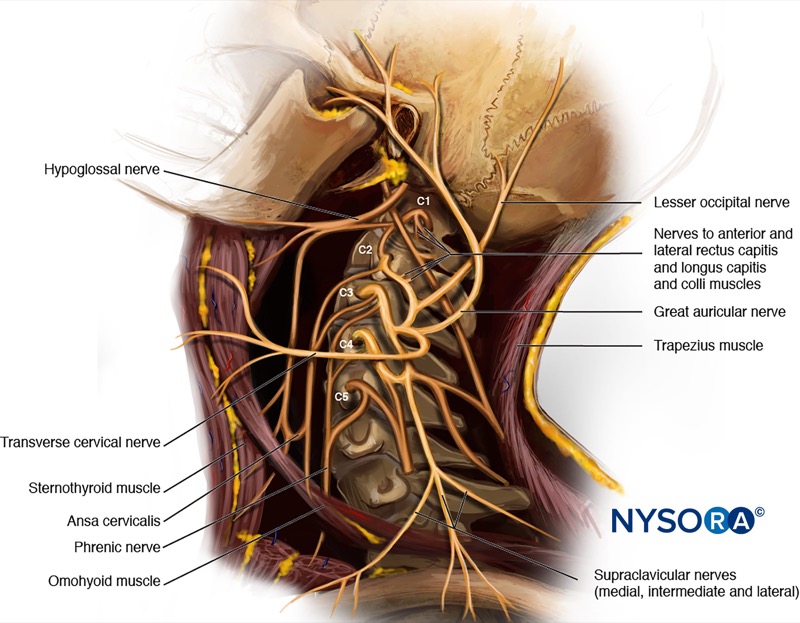
- Slide the transducer cranial and caudally to identify the superficial branches of the cervical plexus as a small collection of hypoechoic nodules (yellow arrows) located under the SCM.
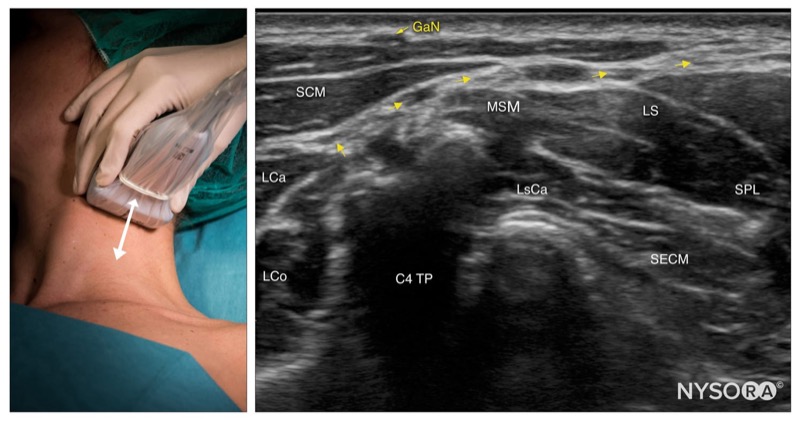
GaN, greater auricular nerve; SCM, sternocleidomastoid muscle; LCa, longus capitis muscle; LCo, longus Colli muscle; MSM, middle scalene muscle; LsCa, longissimus capitis muscle; LS, levator scapulae muscle; SPL, splenius capitis muscle; SECM, semispinalis capitis muscle.
Needle insertion
- Insert the needle in-plane through the skin, platysma, and investing layer of the deep cervical fascia.
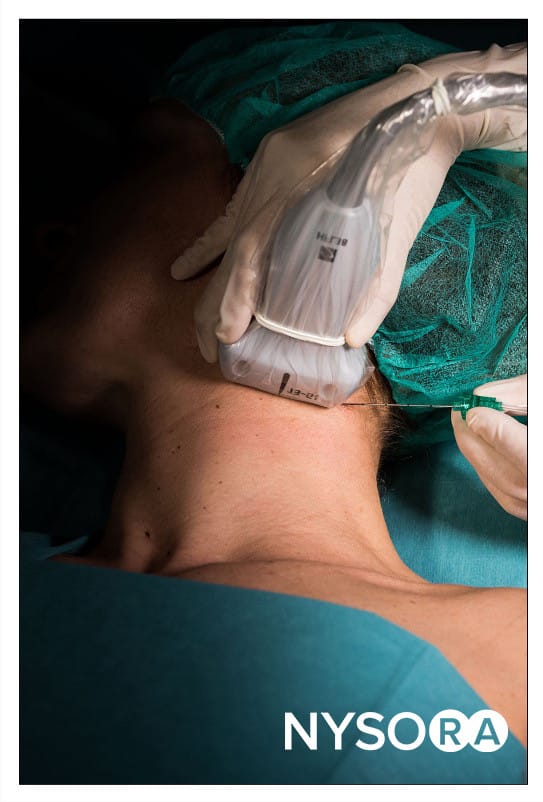
- Position the needle tip behind the posterior border of the SCM.
- Inject 1–2 mL of local anesthetic to confirm proper distribution between the fascial layers containing the branches of the cervical plexus.
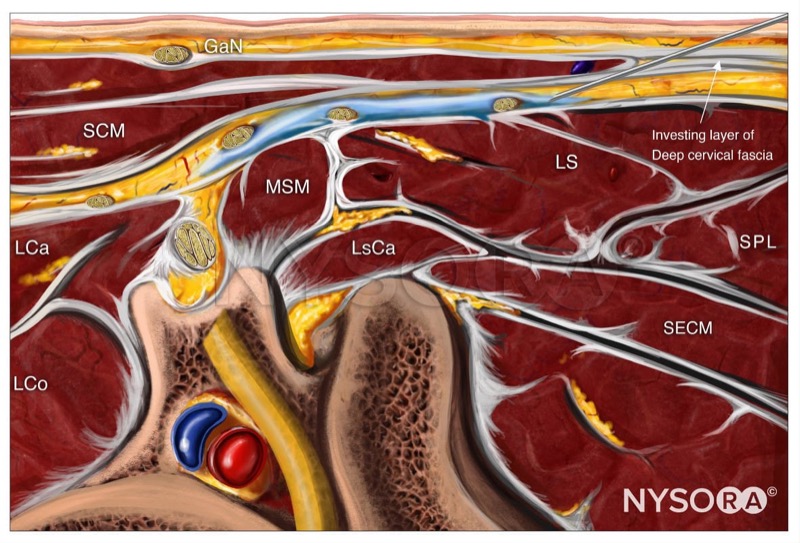
GaN, greater auricular nerve; SCM, sternocleidomastoid muscle; LCa, longus capitis muscle; LCo, longus Colli muscle; MSM, middle scalene muscle; LsCa, longissimus capitis muscle; LS, levator scapulae muscle; SPL, splenius capitis muscle; SECM, semispinalis capitis muscle.
- Complete the block with 5-8 mL.
Alternative transducer position
- Place the transducer in a coronal orientation over the SCM to obtain a longitudinal view.
- Insert the needle in-plane towards the space behind SCM, superficial to the prevertebral fascia.
- Inject 1-2 mL of local anesthetic to confirm needle position.
- Complete the block with a volume of 5-8 mL.
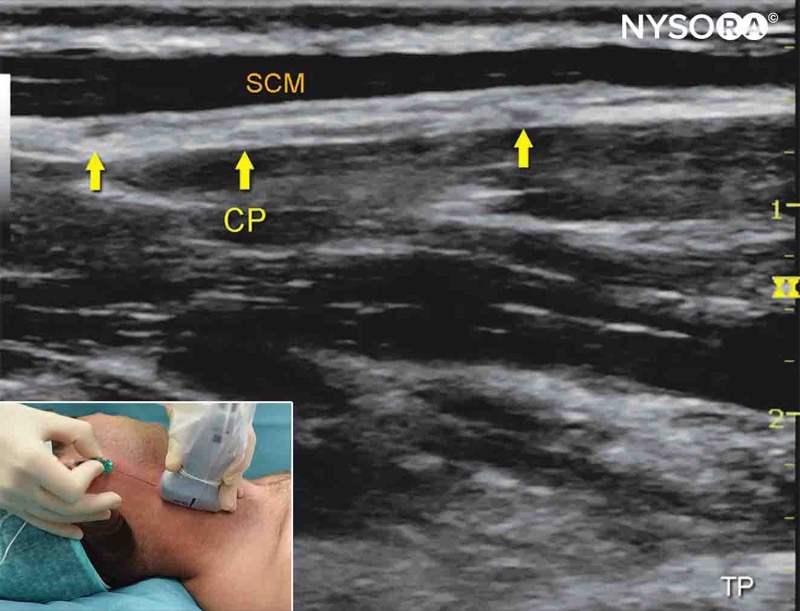
Alternative longitudinal approach for an intermediate cervical plexus block. CP, cervical plexus; SCM, sternocleidomastoid muscle.
Let's review the block:
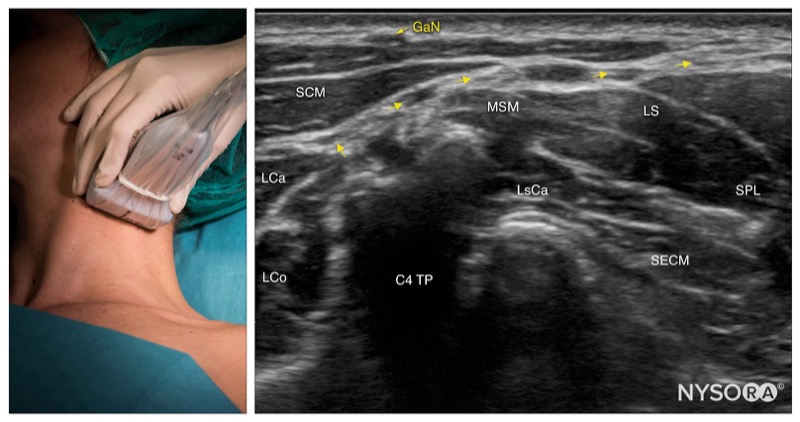
Intermediate cervical plexus; transducer position and sonoanatomy at the C4 level. GaN, greater auricular nerve; SCM, sternocleidomastoid muscle; LCa, longus capitis muscle; LCo, longus Colli muscle; MSM, middle scalene muscle; LsCa, longissimus capitis muscle; LS, levator scapulae muscle; SPL, splenius capitis muscle; SECM, semispinalis capitis muscle.
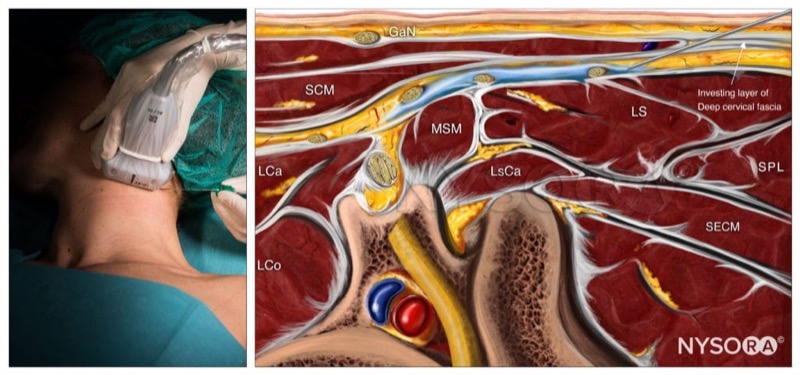
Intermediate cervical plexus block; Reverse Ultrasound Anatomy. GaN, greater auricular nerve; SCM, sternocleidomastoid muscle; LCa, longus capitis muscle; LCo, longus Colli muscle; MSM, middle scalene muscle; LsCa, longissimus capitis muscle; LS, levator scapulae muscle; SPL, splenius capitis muscle; SECM, semispinalis capitis muscle.
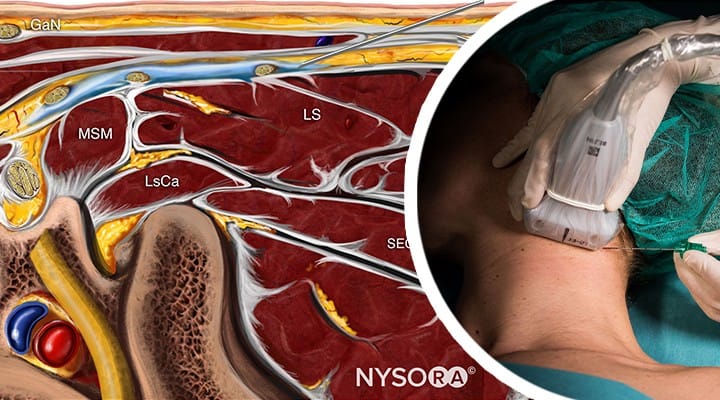



.jpg)